In my journey in the world of digital security, I’ve come across myriad terms and concepts, each with its own depth and significance.
One such distinction, often misunderstood, is between cryptography and encryption.
In this article, I’ll explain the Cryptography vs Encryption match and identify their roles and relevance in data protection.
So why delay? Let us begin and understand the ins and outs of cryptography and encryption!
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is the art and science of hiding information, ensuring that only the designated recipient can interpret it. Think of it as an intricate code system.
This process transforms ordinary text into an encrypted version, known as “ciphertext,” guided by specific procedures termed algorithms.

Deciphering this encrypted text necessitates a unique key. Imagine converting an easily understood note into a confidential message that only select individuals can decipher. This transformation is pivotal for preserving the confidentiality and integrity of information.
The variety in algorithms provides diverse security layers, ranging from verifying the message’s authenticity to maintaining its secrecy.
Types of Cryptography
Picture cryptography as a covert dialect, fortifying our communications against unwanted intrusions.
The three primary categories are:
- Symmetric Key Cryptography: Utilizes a single key for both encryption and decryption. The key needs to remain private. Examples include AES and DES.
- Asymmetric Key Cryptography: Employs two keys – a public key for encryption and a private one for decryption. Widely used in digital signatures and SSL/TLS.
- Hash Function: Converts input data into a fixed-size string of characters, typically a hash value. It’s one-way, meaning you can’t retrieve the original data from the hash. Common in data verification.
What is Encryption?
Encryption is a mechanism in cybersecurity that transforms readable text (plain text) into an indecipherable format, ensuring it can only be interpreted by someone with the appropriate decryption key.
Given the vast amounts of data constantly being exchanged and stored online, encryption is a pivotal line of defense.
From buying office supplies online to accessing an HR portal, our personal information invariably gets integrated into an organization’s networked system, emphasizing the need for robust encryption.
Encryption Types
Encryption keys, underpinned by algorithms, are essentially a sequence of numbers pivotal for encrypting and decrypting data. These keys are unique and randomized.
Primarily, there are two encryption systems:
Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric encryption uses one key to change data into secret code and back again. The key can be set or chosen randomly.
There are two ways to use it: one that codes significant parts of data and another that codes piece by piece. It’s fast because the key is short.
Asymmetric Encryption
Public key cryptography uses two keys: a public one everyone can see and a private one only for the receiver. Encrypting with the public key means only the right receiver can read it. The private key checks who sent the message.
It’s safer but slower than another method, symmetric encryption. Both methods work together for today’s security.
How Does Encryption Work?
Encryption changes regular messages, like texts or emails, into a secret code. This keeps the information safe, whether saved on a computer or sent over the internet.
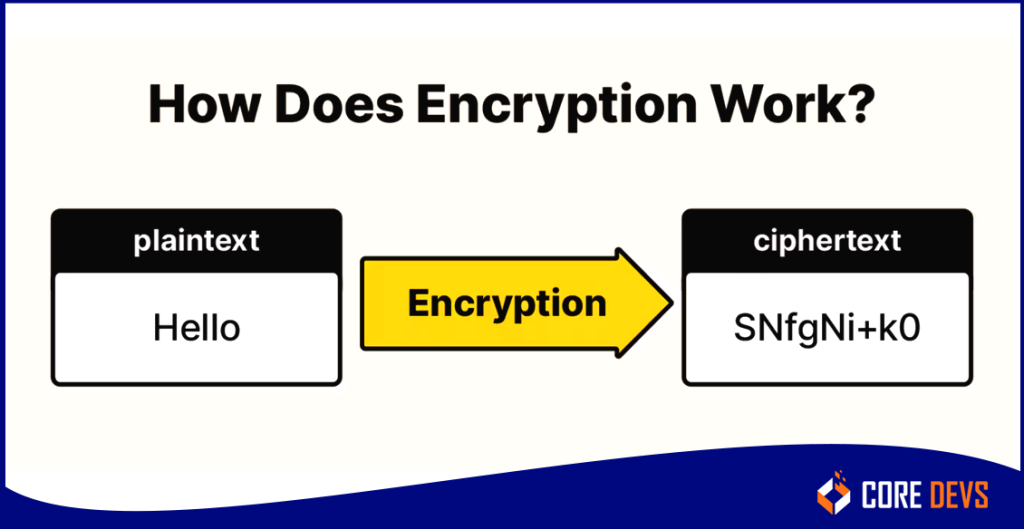
A picture shows how this process works. To read the secret message, the receiver changes it back to the normal message. This is called decryption.
To change and read the message, both the person sending and the person receiving use a special secret code. This code helps turn the message from secret code back to normal and vice versa.
Cryptography vs Encryption: Which One Do You Need to Secure Your Data?
Many see it as interchangeable, even though they serve distinct functions in safeguarding data.
The table below concisely and contrasts cryptography and encryption based on various parameters.
| Basis of Comparison | Cryptography | Encryption |
| Definition | Study of techniques like encryption and decryption. | A process of encoding a message. |
| Nature | A field of study. | A mathematical operation. |
| Basis | Relies on mathematics and algorithm concepts. | Uses concepts like cipher, ciphertext, and key. |
| Utilization | Used for digital signatures and security algorithms. | Used to facilitate secret communication. |
| Category | Symmetric and public key cryptography. | Symmetric and public key schemes (similar to cryptography). |
| Message Verification | Covers encryption and other techniques. | A subset of cryptography that uses a specific algorithm. |
So, Which One Do You Need?
In reality, choosing one over the other is not a matter. Instead, it’s about understanding their interconnectedness. Encryption is your go-to if you want to protect data from prying eyes.
However, if you’re discovering more about digital security, considering aspects like authentication or ensuring data hasn’t been altered, you’re venturing into the broader domain of cryptography.
Real-world Applications and Examples
The significance of cryptography and encryption becomes evident when we observe their applications in our daily lives. These technologies permeate various sectors, ensuring data protection, authentication, and secure communication.
Let’s explore some real-world applications and examples:
How and where cryptography is used?

Here are some places where Cryptography is used:
1. Secure Communications
With the digital era’s rise, the need for secure communication channels has grown immensely. Cryptography ensures that information shared over networks remains confidential and hasn’t been tampered with.
Examples:
- Messaging Apps: Platforms like WhatsApp, Signal, and Telegram employ end-to-end encryption. This means only the sender and recipient can read the message, ensuring privacy.
- Secure Email Services: Tools like PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) or S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) allow users to send encrypted emails, ensuring that only the intended recipient can decrypt and read the content.
- SSL/TLS: Websites use SSL/TLS protocols to encrypt data transmitted between the server and the client, such as login credentials or personal information.
2. Digital Identities
As interactions move online, proving one’s identity digitally becomes crucial. Cryptography helps in verifying the authenticity of users and devices.
Examples:
- Digital Signatures: Used in documents and transactions to verify the signer’s identity and ensure that the document hasn’t been altered after signing.
- Digital Certificates: Issued by Certificate Authorities (CA), these verify the owner’s identity and provide the public key to establish secure communications.
- Authentication Protocols: Protocols like OAuth employ cryptographic techniques to ensure users are who they claim to be when logging into various online services.
3. Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized platforms and need secure methods to verify transactions and ownership without centralized authorities.
Examples:
- Bitcoin & Blockchain: Cryptography validates and adds transactions to the blockchain. It ensures transaction integrity and user anonymity. Public and private keys are used to create digital wallets and sign transactions.
- Smart Contracts: Used in platforms like Ethereum, these self-executing contracts have terms directly written into code lines. Cryptography ensures that the code remains immutable once deployed and executes as intended.
- Proof of Work/Stake: Cryptographic puzzles are at the heart of these consensus algorithms, determining who can add the next block in blockchain platforms.
If you want to learn more about how cryptocurrencies function, do not forget to check out our latest blog that illustrates the working process of cryptocurrencies.
How and where is encryption specifically applied?
Here are 3 major applications of Encryption:
1. Securing Data in Transit
As data travels between devices or across networks, it’s vulnerable to interceptions. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unintelligible to unauthorized entities.
Examples:
- SSL/TLS for Web Traffic: When you visit a website starting with “https”, it means the data exchanged between your browser and the server is encrypted using SSL/TLS. This ensures activities like online shopping, banking, or simply browsing remain private and secure.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs encrypt internet traffic, ensuring data remains confidential and secure from potential eavesdroppers, especially on unsecured public networks.
2. Securing Data at Rest
Data stored on devices can be vulnerable to theft or unauthorized access. Encryption ensures that stored data remains unreadable without the correct decryption key.
Examples:
- Encrypted Hard Drives: Modern computers and external hard drives often have built-in encryption tools like BitLocker (Windows) or FileVault (Mac) that encrypt the entire storage drive.
- Database Encryption: Databases storing sensitive information, like user credentials or personal details, use encryption to protect data from breaches or unauthorized access.
- Cloud Storage: Services like Dropbox, Google Drive, and iCloud encrypt user data, ensuring that files stored in the cloud are protected against unauthorized access.
3. Messaging Apps
In the age of digital communication, ensuring the privacy of personal and professional conversations is crucial. Encryption ensures that only the intended recipients can read the messages.
Examples:
- WhatsApp: This popular messaging app employs end-to-end encryption. When a message is sent, it’s encrypted on the sender’s device and only decrypted on the recipient’s device, ensuring utmost privacy.
- Signal: Like WhatsApp, Signal provides end-to-end encryption for messages, calls, and even video chats, ensuring that no one, not even Signal itself, can access the communication content.
- Telegram: While Telegram offers general encryption, users can also opt for “Secret Chats”, which uses end-to-end encryption and leaves no trace on Telegram’s servers.

Core Devs Offers Cryptograph solutions for any kind of SaaS you can name. Talk to us today!
Final Thoughts
When the topic is Cryptography vs Encryption, we’re diving into how we keep our online stuff safe.
Cryptography is like a big umbrella, and encryption is one tool under it. Both are super important for keeping our messages, photos, and data safe from hackers.
So, next time you’re online, remember these two are working behind the scenes to protect you!
